How To Create Moving Animation In Maya
When you keyframe an object's rotations, Maya calculates the object's orientations between keys by interpolating the rotation values from one key to the next. In Maya, at that place are two methods of rotation interpolation: Euler and Quaternion. For each animated rotation in your scene, you can specify a rotation interpolation method. The rotation interpolation method yous cull for an blithe object determines how Maya calculates its rotations. For more data on Euler angles and Quaternions, see Euler angles, Quaternions, and Which blazon of interpolation is right for your animated rotations?.
Euler rotation is the default method of rotation interpolation unless otherwise specified. You can set the default rotation interpolation method for new curves in the Maya window (in the section under the category when you lot select ) or yous can prepare the rotation interpolation method of existing rotation curves from the . Come across Prepare rotation interpolation for curves.
Euler angles
When interpolating the animated rotations of an object using the Euler method, Maya uses Euler angles to determine the object's axis-specific orientations over fourth dimension. Euler rotations are calculated using three separate angles representing rotations about the 10, Y, and Z axes, and an order of rotation.
The rotation gild specifies the society in which an blithe object is rotated about its X, Y, and Z axes. Changing an animated object's rotation order changes its final orientation. Y'all tin specify the society of rotation for an object by setting its aspect. For instance, if you lot set an animated object's to YZX, the object will first rotate in Y, then Z, and finally X. You can utilise the attribute to match the rotation order of imported, animated objects to the co-ordinate systems (for instance, XZY opposed to Maya's default XYZ) of the 3D software packages from which they came. This is important if you want the animated rotations of your imported objects to appear every bit intended.
In Maya, the default method of rotation interpolation is Euler.
At that place are 2 kinds of Euler rotation interpolation in Maya: Contained and Synchronized. You tin gear up the Euler rotation interpolation type for your curves from the . See Change Rotation Interp.
For curves, interpolation is calculated from key to central on each private curve, independent of the their neighboring rotation curves. Utilise curves when you want to keyframe a single rotation channel or when you lot need to add boosted keyframes (and thus detail) to a single rotation curve. curves are ideal for simple, animated rotations.
All the keyframes on curves are locked together in fourth dimension. This ways that if an object has rotation curves, interpolation is calculated from key to key on all of its rotation curves simultaneously. Utilize curves when yous desire to keyframe multiple rotation channels (10, Y, and Z) or when you need to add boosted keyframes (and thus detail) to all the rotation curves of an blithe object. curves are ideal for more circuitous blithe rotations.
The main difference between and curves are their keyframes. For example, moving a key in time on an curve moves merely the key on the bend, whereas moving a key in time on a curve will also move the respective keys on the and curves. Similarly, if you key only the channel for an animated object, and the rotation interpolation type is gear up to , and so but the channel is keyed. Even so, if the rotation interpolation type is set to , then all three (, , and ) channels are keyed.
When Euler angles are used to interpolate the animated rotations of an object, the object's orientation about its private axes is evaluated one axis at a time. This is why Euler-angled rotation is prone to artifacts such as gimbal lock and flipping. Gimbal lock occurs when rotations about a unmarried axis cause unwanted rotations near complementary axes or when axes go coincident. Flipping occurs when angles unexpectedly wrap effectually positive or negative 180 degrees during Euler-angled rotation interpolation between keyframes.
If gimbal lock or flipping occurs, you may be able to correct this beliefs using the . For instance, you tin use the to normalize the mangled rotation curves from corrupted move capture animation data. You can access the from the menu in the or . For more information on the , run across Euler angle filtering and filterCurve.
When should I use Euler rotation interpolation?
Use Euler rotation interpolation when you want specific control over the numerical values of your rotations and when yous desire smooth tangents for your rotation curves. In most cases, you should only use Euler rotation interpolation for rotation animation curves that you demand to dispense extensively in the . Unlike Quaternion curves, Euler curves support all tangent types and their keys possess tangent handles that let you easily tweak the curves.
Quaternions
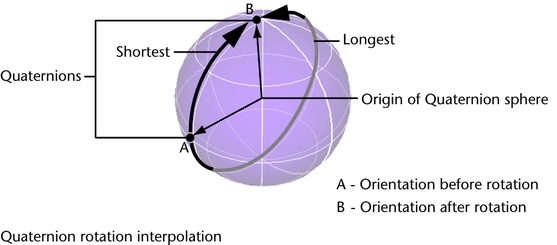
Quaternions provide polish interpolation of animated rotations and always produce the near efficient path between keyframes in comparison to Euler angles. Quaternions store the overall orientation of an object rather than a serial of private rotations. This means that a single Quaternion stores the same amount of rotation data as three Euler angles. Since Quaternions store only orientation values, they tin be used to calculate the shortest rotation from one orientation to some other.
When animating an object's rotations with , Maya beginning stores the keyed orientation values for the object every bit Euler angles, converts them to Quaternions for interpolation, and so converts the interpolated Quaternion rotation values back to Euler angles for display in the and .
In Maya, Quaternions are displayed equally curves and values. When an object's rotation curves are synchronized, the keyframes on its ,, and curves are locked together in fourth dimension. When yous add, delete, or movement a keyframe on i of the object's rotation curves, the respective keys are too updated on the related rotation curves. This eliminates unexpected interpolation problems that can occur when keyframes are deleted from i of the axes, or when keys are moved independently in time.
The tangent settings for Quaternion curves affect how an object'southward animated rotations are interpolated. For more information on tangent types, come across Graph Editor Tangents menu. Maya uses the following types of tangents and interpolation to calculate the shortest rotation from ane central to the next:
- Quaternion curves with clamped tangents use stepped interpolation
- Quaternion curves with linear tangents use spherical linear interpolation (likewise known as SLERP)
- Quaternion curves with spline tangents utilise cubic interpolation
For Quaternion curves with clamped tangents, Maya uses stepped interpolation. For Quaternion curves with linear tangents, Maya uses spherical linear interpolation—also known as SLERP—to calculate the shortest rotation from one key to the side by side and produces an precipitous transition between keys. For Quaternion curves with spline tangents, Maya uses cubic interpolation to calculate the shortest rotation from 1 fundamental to the next and produces a smooth transition between keys.
When blending animation clips in the Maya ® ™ , yous can select i of the post-obit types of Quaternion rotation interpolation: or . interpolation uses Quaternion interpolation to observe the shortest path between rotations from one clip to the next. interpolation uses Quaternion interpolation to detect the longest path between rotations from ane clip to the next. This path is in the reverse direction of .
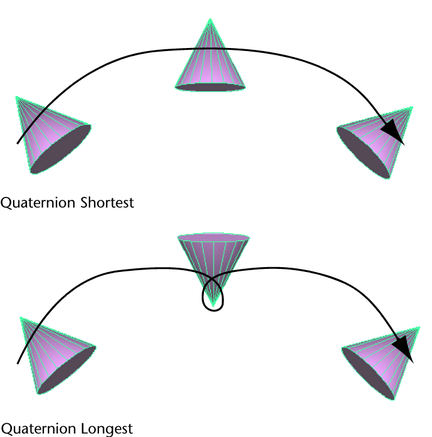
You can specify a clip blend's Quaternion rotation interpolation type from the by setting the blend'south attribute.
When should I use Quaternions?
Apply Quaternions when you want smooth interpolation between 2 keys. Quaternions produce the most efficient paths of interpolation and they do not generate artifacts such every bit gimbal lock and flipping.
Warning
- It is difficult to isolate, view, and edit Quaternion curves in the .
- Quaternion curves do non support tangent handles and merely work well with linear tangents.
Which type of interpolation is right for your animated rotations?
Each method of rotation interpolation has its advantages and disadvantages. Information technology is upwardly to you to select the blazon of interpolation that best suits your animation. Meet When should I use Euler rotation interpolation? and When should I use Quaternions?.
| Euler angles | Quaternions | |
|---|---|---|
| Advantages |
|
|
| Disadvantages |
|
|
Note
Whether your object's rotations use Quaternions or Euler angles, the volition e'er display Euler angle values.
Except where otherwise noted, this piece of work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License
Source: https://download.autodesk.com/global/docs/maya2014/en_us/files/Animation_Basics_Animated_rotation_in_Maya.htm
Posted by: hansoneachich.blogspot.com

0 Response to "How To Create Moving Animation In Maya"
Post a Comment